Grasping the mechanics and applications of heat exchangers is essential for engineers and businesses looking to enhance their processes. From the intricacies of different types of heat exchangers to the importance of proper maintenance, the future of this technology is intertwined with creativity and sustainability. This article will explore the latest advancements, applications, and the significant role heat exchangers will play in shaping an energy-efficient future.
Comprehending Heat Transfer Devices
Thermal exchangers are vital units used to transfer thermal energy between multiple fluids without blending them. Their chief function is to enable efficient thermal energy exchange, enhancing heating or cooling systems across various applications. These devices utilize different methods of heat transfer, such as conduction, convection, and occasionally radiation, to reach the target temperature modifications in industrial or corporate settings.
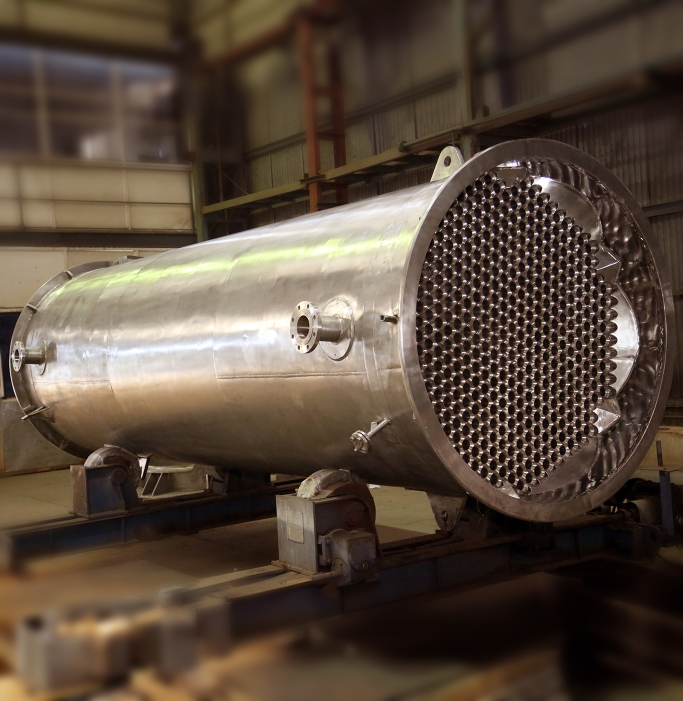
There are numerous types of heat exchangers, all designed for certain uses and varying in magnitude, complexity, and efficiency. Common types include shell and tube, plate, finned tube, and air-cooled units. All types offers unique benefits and cons, allowing engineers to pick the most appropriate option based on criteria like space requirements, fluid characteristics, and operational settings. Comprehending Standard Xchange is essential for maximizing the efficiency of energy solutions.
In the last years, developments in heat exchanger technology have aimed on enhancing energy efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. Innovations such as improved materials, compact designs, and digital monitoring systems are evolving traditional concepts into better and sustainable choices. As sectors continue to adopt energy efficiency, the role of heat exchangers is becoming increasingly important for reaching lower operational costs and meeting global sustainability targets.
Applications and Benefits
Heat transfer devices play a vital role across various industries, providing efficient methods for transferring heat between fluids. In the chemical industry, for example, they are essential for maintaining ideal temperatures during processes, thus boosting product quality and safety. Similarly, in the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning sector, heat exchangers are crucial for managing indoor climate and enhancing energy efficiency. Their ability to recapture and utilize thermal energy significantly lowers overall energy consumption, making them an key part of green building designs.
One of the prominent roles of heat exchangers is in food and beverage processing. Here, they ensure that products are heated or chilled rapidly while maintaining quality and safety standards. Their design allows for exact temperature control, which is crucial for procedures such as pasteurization and chilling. Additionally, the use of gasketed plate heat exchangers in this sector not only boosts heat transfer capabilities but also allows for simple maintenance and cleaning, thus meeting hygiene regulations.
The gains of using heat exchangers extend beyond operational efficiency; they also result in cost savings and improved sustainability. By enhancing energy use and reducing wastage, facilities can significantly lower their operating costs. Moreover, with advancements in components and layout, modern heat exchangers are becoming even more streamlined and efficient, making them suitable for a broader range of applications, including sustainable energy systems. As industries continue to focus on sustainability, the demand for novel heat exchanger solutions that meet particular needs will definitely increase. ### Future Innovations and Trends
As sectors put greater emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability, heat exchangers are evolving through innovative designs and advanced materials. The incorporation of digital technologies is revolutionizing how heat exchangers are observed and serviced. Smart sensors and IoT solutions allow for real-time performance tracking, facilitating predictive maintenance which minimizes downtime and improves overall efficiency. This transition not only minimizes operational costs but also extends the durability of these essential components.
In response to the growing demand for environmentally friendly solutions, manufacturers are investigating the use of innovative materials in heat exchanger design. Advanced polymers and composites are being evaluated for their thermal performance and corrosion resistance, opening new possibilities for applications across various industries. Additionally, research into 3D printing technologies is gaining momentum, offering custom heat exchanger designs that can meet specific industrial needs while reducing waste and production costs.
The future of heat exchanger technology will also focus on compact and lightweight designs. Innovations in heat transfer efficiency aim to maximize performance while minimizing the physical footprint of these systems. This trend is particularly beneficial in sectors such as automotive engineering and renewable energy, where space constraints are prevalent. As these advancements unfold, heat exchangers will play a pivotal role in driving energy-efficient practices and promoting sustainability across global industries.
